Your Location:Home > Products > Food Ingredients > D-Galactose


CasNo: 59-23-4
MF: C6H12O6
Appearance: white.
|
Biological Activity |
Galactose is a simple monosaccharide that serves as an energy source and as an essential component of glycolipids and glycoproteins. Galactose contributes to energy metabolism via its conversion to glucose by the enzymes that constitute the Leloir pathway. Defects in the genes encoding these proteins lead to the metabolic disorder galactosemia. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Galactose is a simple monosaccharide that serves as an energy source and as an essential component of glycolipids and glycoproteins. Galactose contributes to energy metabolism via its conversion to glucose by the enzymes that constitute the Leloir pathway. Defects in the genes encoding these proteins lead to the metabolic disorder galactosemia. |
|
Purification Methods |
D-Galactose is crystallised twice from aqueous 80% EtOH at -10o, then dried in a vacuum oven at 90o over P2O5 for 10hours. [Link Biochemical Preparations 3 75 1953, Hansen et al. Biochemical Preparations 4 2 1955.] Also purify it by recrystallising the dried solid (150g) in hot H2O (150mL), then adding hot MeOH (250mL) and hot EtOH (500mL), stirring to mix, filtering through a bed of charcoal, and the clear filtrate is stirred to initiate crystallisation. After standing overnight at 10o, the crystals of the -anomer are filtered off by suction, washed with MeOH, then EtOH, and dried (yield 130g), and more can be obtained by evaporation of the filtrate and washing as before. [Wolfrom & Thompson Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry I 120 1962, Academic Press, Beilstein 1 IV 4336.] |
|
General Description |
D-Galactose, also known as Galactose, D- (8CI), (+)-Galactose, or D-(+)-Galactose, is a monosaccharide that serves as a key component in various biochemical and synthetic applications. It is utilized in the synthesis of chiral ligands for asymmetric catalysis, fluorescent probes for enzyme studies, immunosuppressive marine glycosphingolipids like Plakoside A, and drug-carrying cyclodextrin conjugates for targeted delivery. Its derivatives are involved in heterocyclization reactions and are recognized by galactosyltransferases, highlighting its versatility in organic and medicinal chemistry. |
|
Definition |
A monosaccharide commonly occurring in milk sugar or lactose. |
|
Application |
Galactose has been used:as a component of galactosyltransferase labeling buffer.as a supplement in MRS broth for the growth of thermophilic lactobacilli.to induce the expression of uncoupling protein (UCP) in yeast transformants. |
InChI:InChI=1/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h1,3-6,8-12H,2H2/t3-,4+,5+,6-/m0/s1
p-Hydroxybenzoyl β-galactose (pHB-Gal) w...
Bifidobacteria are predominant in the in...
A supported ionic liquid phase (SILP) ca...
The intracellular β-galactosidase (β-gal...
Adxanthromycins A and B are new inhibito...
Chromatographic purification of the extr...
Dress code for living in a fungus: Analy...
To identify active compounds in the root...
The new cycloartane glycoside cyclotanos...
The O-polysaccharide obtained by mild ac...
beta-D-Galactosidase from Aspergillus ni...
-
-
High molecular weight crude and purified...
Two new cucurbitane triterpenoids 1 and ...
Houttuynoid M (1), a new houttuynoid, an...
Globally, one in six deaths is reported ...
In this study, apple pectin (AP) and tom...
The phytochemical investigations of the ...
Two previously undescribed steroidal alk...
Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides (SFP...
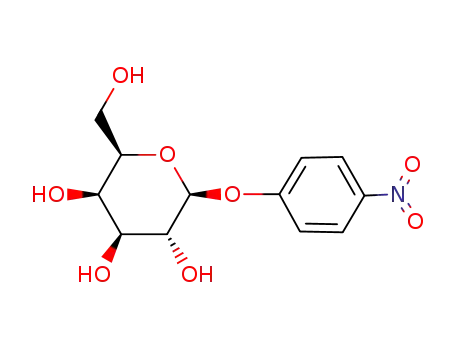
4-nitrophenyl-β-D-galactopyranoside

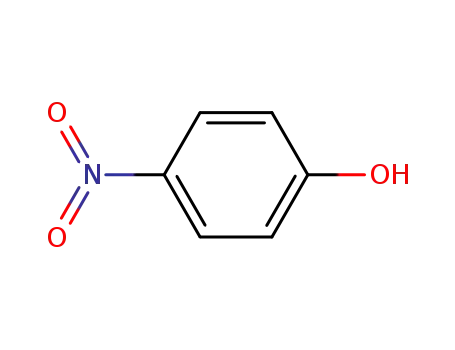
4-nitro-phenol
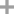
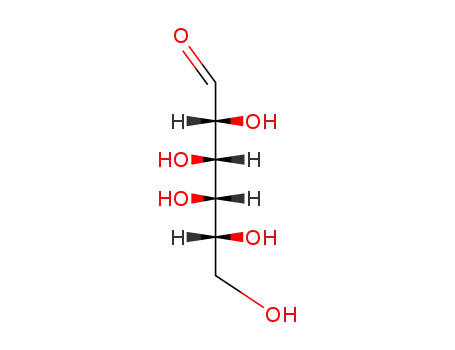
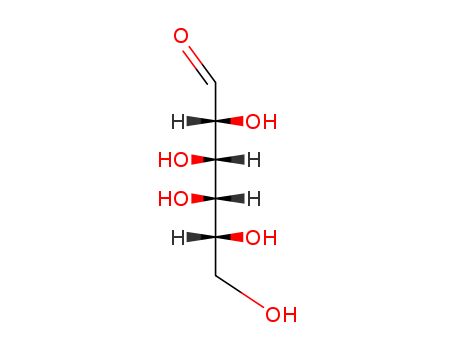
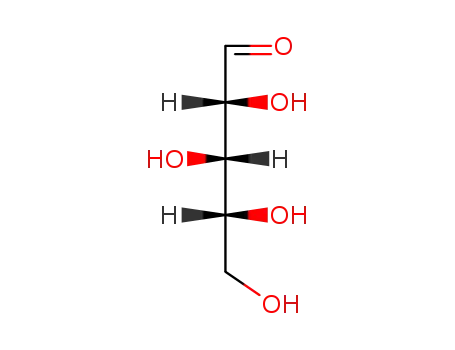
D-Galactose
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
water;
for 0.333333h;
Rate constant;
acetate buffer pH 4.5, β-D-galactosidase;
|
|
|
With
β-D-galactosidase; sodium phosphate buffer;
at 37 ℃;
pH=7.2;
Further Variations:;
Reagents;
Enzyme kinetics;
|
|
|
With
recombinant Paecilomyces aerugineus β-galactosidase;
at 55 ℃;
for 0.0833333h;
pH=4.5;
Kinetics;
aq. citrate buffer;
Enzymatic reaction;
|
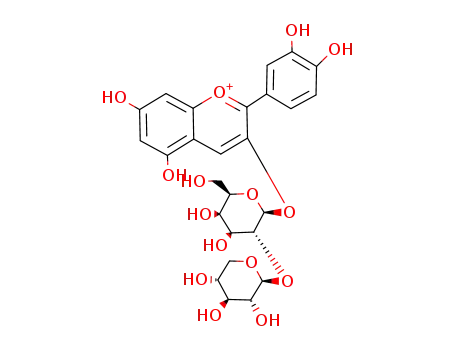
cyanidin 3-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-galactopyranoside

D-xylose

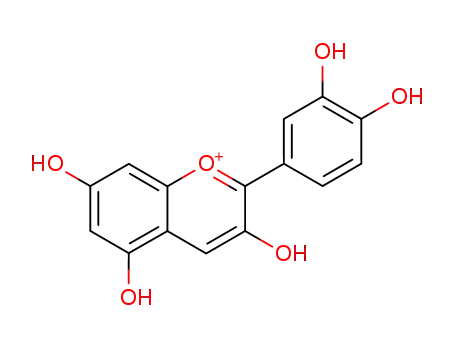
cyanidin


D-Galactose
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; water;
at 95 ℃;
for 2h;
|
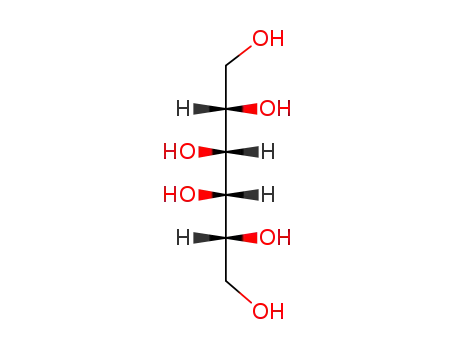
D-galactitol
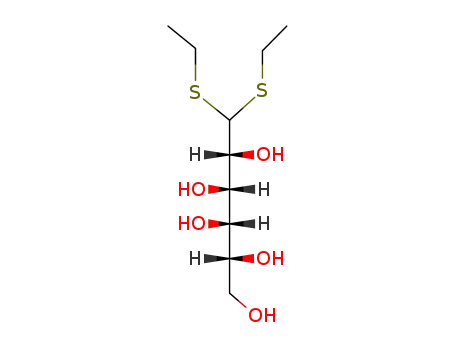
D-galactose-diethyl-dithioacetal
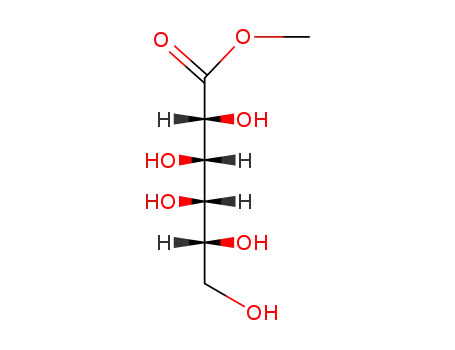
D-galactonic acid methyl ester
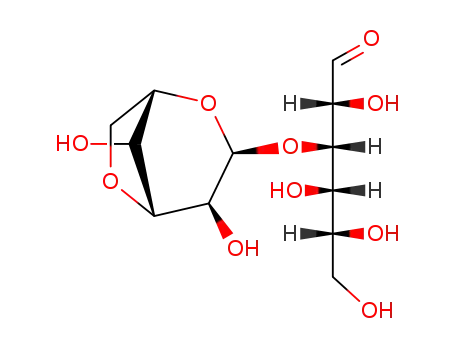
O3-(3,6-Anhydro-α-L-galactopyranosyl)-D-galactose
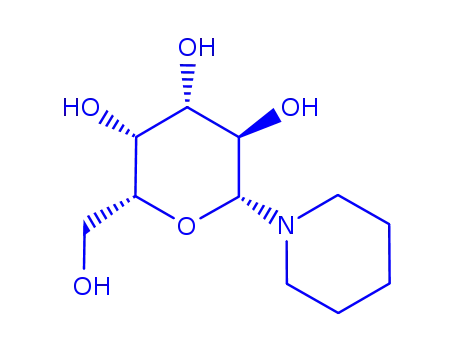
1-β-D-galactosylpiperidine
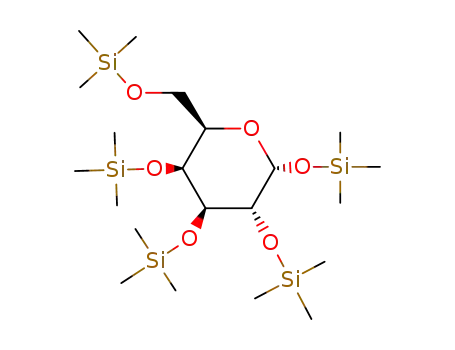
1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-trimethylsilyl-α-D-galactose
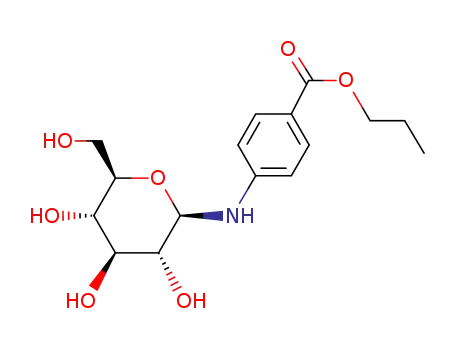
4-β-D-galactopyranosylamino-benzoic acid propyl ester
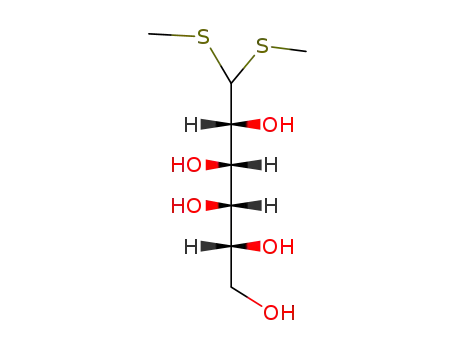
D-Galactose-dimethyldithioacetal