Your Location:Home > Products > Food Ingredients > Arachidonicacid Powder



CasNo: 506-32-1
MF: C20H32O2
Appearance: colorless to light yellow oil
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A long-chain fatty acid that is a C20, polyunsaturated fatty acid having four (Z)-double bonds at positions 5, 8, 11 and 14. |
|
General Description |
A Certified Spiking Solution? suitable for use in mass spectrometry-based fatty acid testing applications such as assessment of cardiovascular disease risk and fatty acid deficiency, and detection and quantification of arachidonic acid in nutraceuticals and dietary supplements. Arachidonic acid (cis-5,8,11,14), sometimes referred to as AA or ARA, is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid. Studies suggests that ARA as well as other fatty acids can serve as biomarkers for cardiovascular disease, and nutritional and metabolic disorders. |
|
Biological Activity |
Endogenous free fatty acid released from phospholipids by phospholipase A 2 . Important cellular signaling mediator and precursor of eicosanoids. Metabolized by lipoxygenases, cyclooxygenases and cytochrome P450 monooxygenases. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Arachidonic acid stimulates adhesion of MDA-MB-435 human metastatic cancer cells to extracellular matrix molecules (collagen IV and vitronectin) . |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous route.Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation datareported. When heated to decomposition it emits acridsmoke and irritating fumes. |
|
Carcinogenicity |
In vitro and in vivo studies indicate that inhibition of arachidonic acid metabolism inhibits the growth of malignant cells, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and implicates arachadonic acid in facilitating the metastasis of these tumor cells. Arachidonic acid reaction with cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenases yield eicosanoids that can mediate prostate cancer proliferation and enhance both tumor vascularization and metastasis. Cytochrome P450 arachidonic acid epoxygenases promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in endothelial cells. |
InChI:InChI=1/C20H32O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20(21)22/h6-7,9-10,12-13,15-16H,2-5,8,11,14,17-19H2,1H3,(H,21,22)/b7-6+,10-9+,13-12+,16-15+
Diacylglycerol lipase-beta (DAGLβ) hydro...
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is the...
Pure arachidonic acid (1) and docosahexa...
Endocannabinoids are endogenous ligands ...
Tailor-made peptides were investigated f...
14,15- Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (14,15-E...
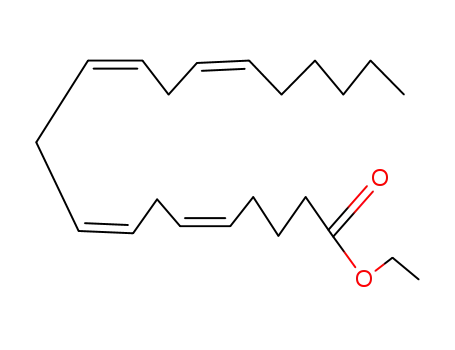
ethyl arachidonate


all cis 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
triethylamine;
In
water; acetonitrile;
at 30 ℃;
for 96h;
under 7500600 Torr;
|
78% |
|
With
potassium hydroxide;
|
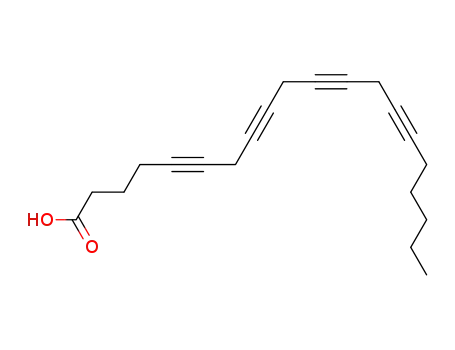
eicosa-5,8,11,14-tetraynoic acid


all cis 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium tetrahydroborate; hydrogen; ethylenediamine;
nickel diacetate;
In
ethanol;
at 20 ℃;
|
34% |
|
With
hydrogen;
Lindlar's catalyst;
In
methanol;
|
|
|
With
quinoline; water; hydrogen;
Lindlar's catalyst;
Yield given. Multistep reaction;
1.) AcOEt;
|
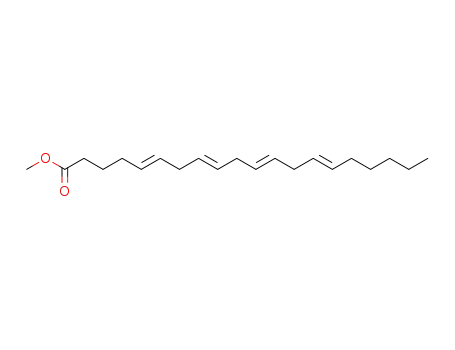
arachidonic acid methyl ester

eicosa-5,8,11,14-tetraynoic acid
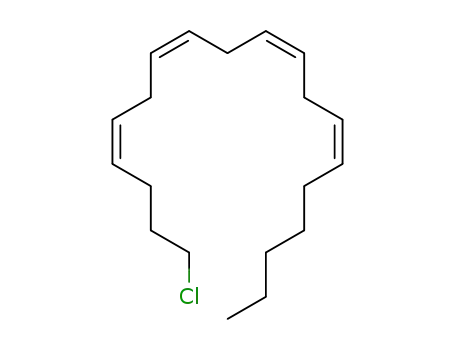
1-chloro-nonadeca-4c,7c,10c,13c-tetraene
carbon dioxide
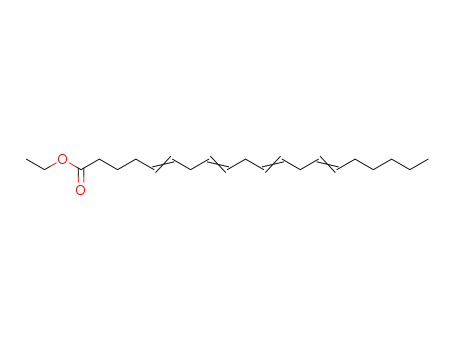
ethyl arachidonate

5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic acid

methyl arachidonate
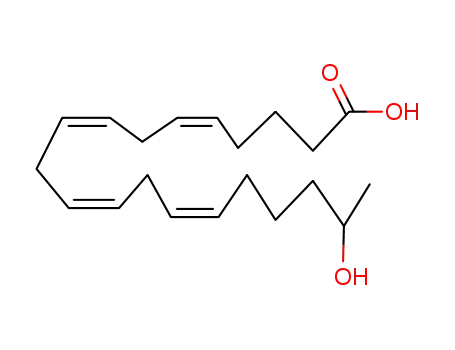
19-Hydroxyarachidonic acid