Your Location:Home > Products > Food ingredients > L-Arabinose
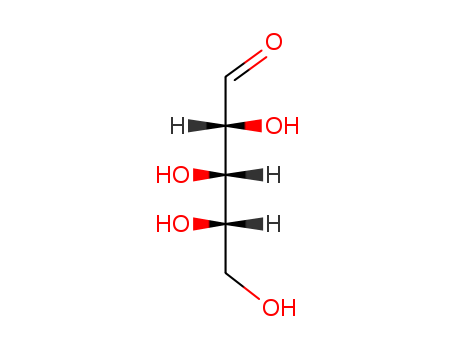


CasNo: 5328-37-0
MF: C5H10O5
Appearance: white crystalline powder
|
Preparation |
By partial hydrolysis of mesquite gum. |
|
benefits |
L-Arabinose can play an important role in the management of blood glucose and insulin levels related to sucrose intake. The addition of L-Arabinose to a sugar containing diet has the following direct benefits: 1) up to 60% reduction of the glucose peak level related to sucrose consumption, 2) up to 60% suppression of the insulin peak level related to sucrose consumption, and 3) a sustained release of glucose to the body over a longer period of time. A low glycemic diet may have benefits like reduction of heart disease, lowering of blood cholesterol, management of body weight and composition, and prevention of type 2 diabetes. A low insulinic diet may lead to lower fat storage and prevention of pre-diabetes incidence. Sustained glucose release over a longer period of time has advantages for athletes and other people that value a responsible and healthy diet. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
|
Biological Activity |
L-Arabinose is the naturally occurring isomer and is a constituent of plant polysaccharides. Most bacteria contain an inducible arabinose operon that codes for a series of enzymes and transporters that allows L-arabinose to be used as the sole carbon source in microbial culture. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
L-(+)-Arabinose is a naturally occurring pentose sugar that has been shown to decrease lipogenesis in rat models due to its ability to inhibit sucrase activity. |
|
Definition |
l-enantiomers occur naturally. lArabinose is common in vegetable gums, especially arabic. |
|
Application |
L-Arabinose is used as a substrate to identify, differentiate and characterize pentose sugar isomerase(s). L-Arabinose is used in the bioproduction of L-ribose.L-(+)-Arabinose is a pentose sugar that occurs naturally in corn fiber gum and acacia gum.L-(+)-Arabinose is used as a key starting material in the total synthesis of (+)-ambruticin, zaragozic acid A, (?)-radicamine B and (+)-herbarumin I. |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H10O5/c6-2-1-10-5(9)4(8)3(2)7/h2-9H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5?/m0/s1
Two new cycloartane triterpenes, cimyunn...
-
Development of stable and recyclable sol...
Antifungal screening of small-molecule n...
Nine new triterpene derivatives, yunnant...
Purification of n-BuOH fraction from 80%...
The chemical investigation of the root b...
A new spirostanol glycoside isolated fro...
Fractionation of the polysaccharide comp...
Two new oleanane-type saponins, 1α-hydro...
A new compound, MK800-62F1, was isolated...
A novel heteropolysaccharide (GCPB-2) wi...
The novel natural low-molecular-mass pol...
Three undescribed oleanane type triterpe...
A novel polysaccharide obtained from Ent...
One new lignan, loniceralanside A (1), t...
![cyanidin 3-O-[6-O-(2-O-(trans-caffeoyl)-α-arabinofuranosyl)-β-glucopyranoside]-7,3'-O-di[6-O-(trans-caffeoyl)-β-glucopyranoside]](/upload/2025/8/f9f26f34-2eee-45df-aee2-3c327c1c3efb.png)
cyanidin 3-O-[6-O-(2-O-(trans-caffeoyl)-α-arabinofuranosyl)-β-glucopyranoside]-7,3'-O-di[6-O-(trans-caffeoyl)-β-glucopyranoside]

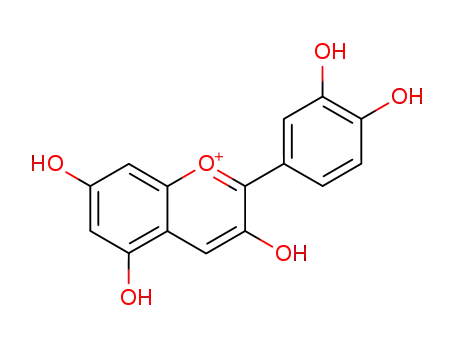
cyanidin
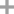
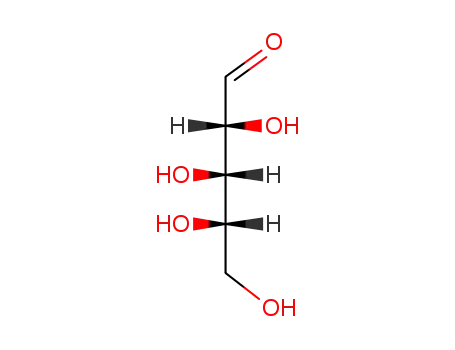
L-arabinose

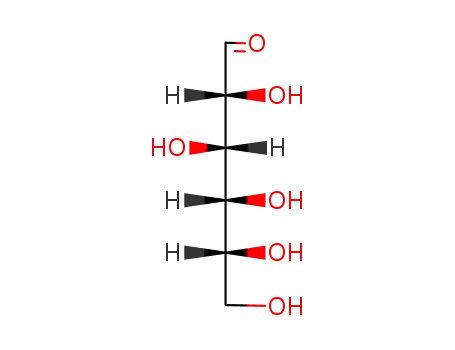
D-glucose

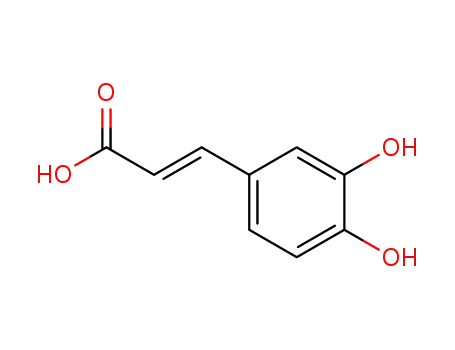
caffeic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Acidic conditions;
|
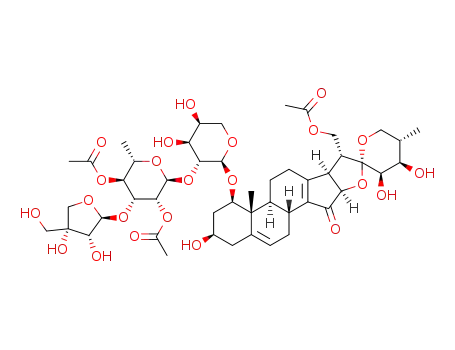
trilliumoside I

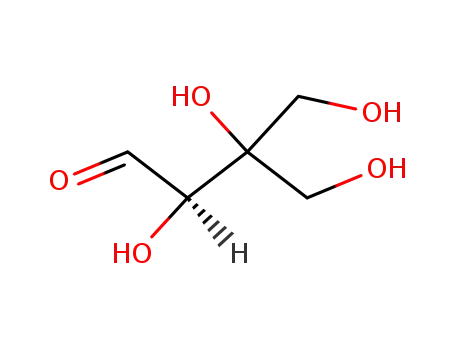
D-apiose


L-arabinose

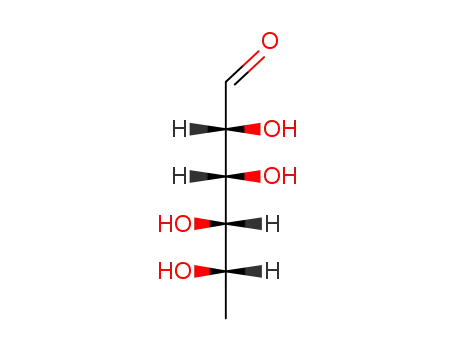
L-Rhamnose
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
trifluoroacetic acid;
In
1,4-dioxane; water;
at 90 ℃;
for 3h;
|
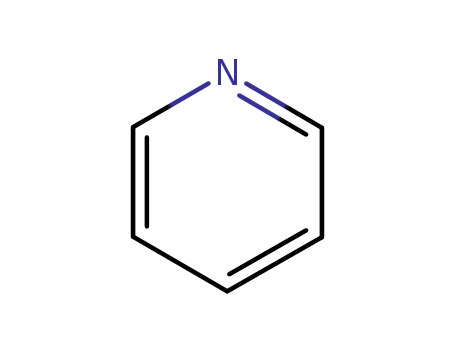
pyridine
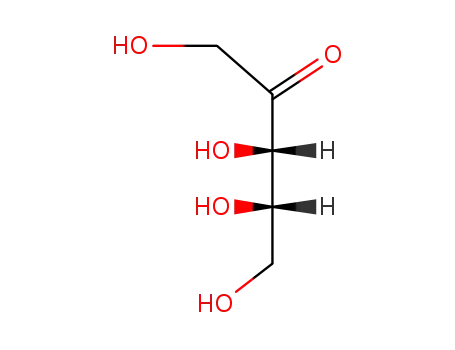
L-ribulose
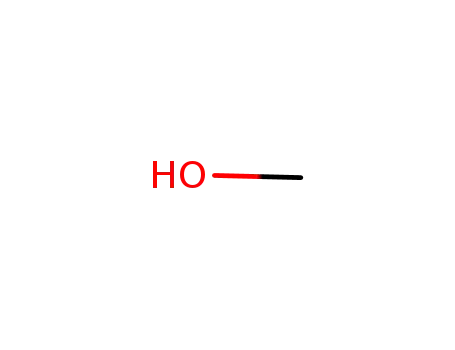
methanol
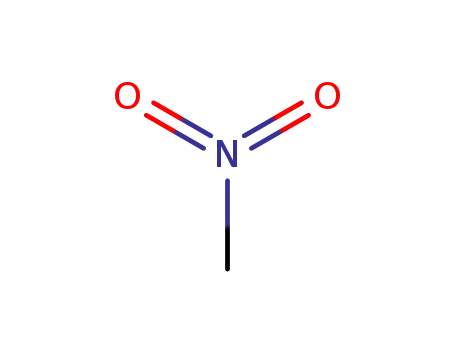
nitromethane
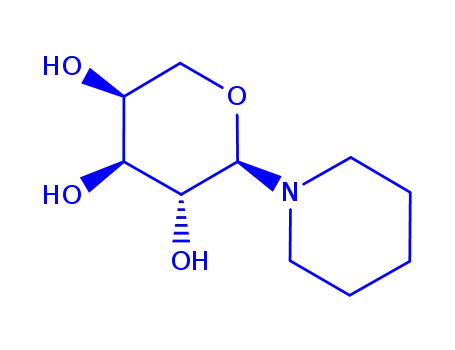
(1R)-1-piperidino-1,5-anhydro-L-arabitol
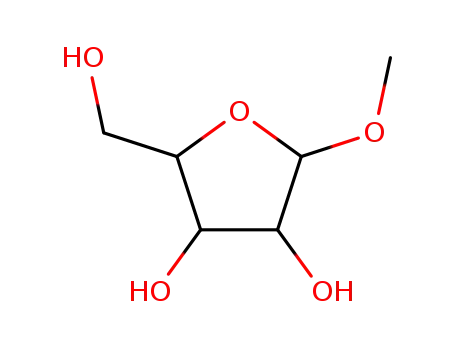
methyl-xylofuranoside
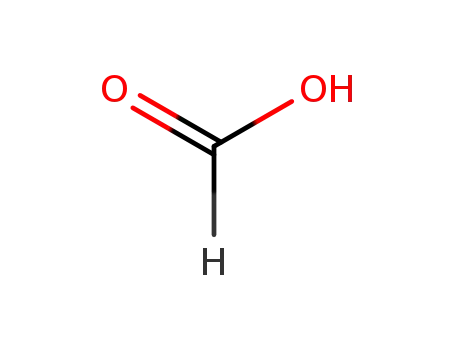
formic acid
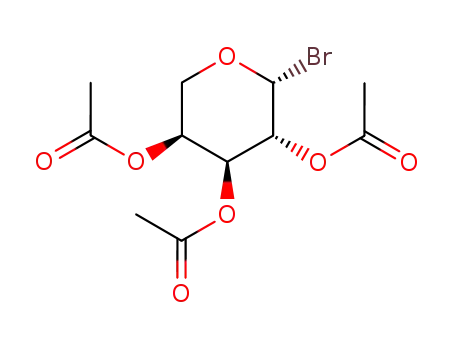
2,3,4-tri-O-acetyl-α-L-arabinopyranosyl bromide