Your Location:Home > Products > Food ingredients > L-Glutamic acid
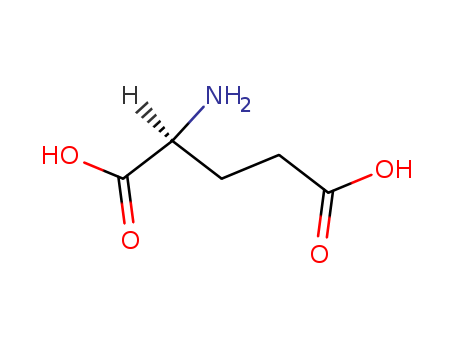


CasNo: 56-86-0
MF: C5H9NO4
Appearance: White cryst. powder
|
Biological Functions |
Glutamic acid serves as a fundamental excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, playing a crucial role in cognitive and sensorimotor functions. It is essential for brain functions and homeostasis. |
|
Role in Plant Development |
Glutamic acid contributes to the development of chlorophyll molecules and is involved in carbohydrate anabolism. It aids in the synthesis of growth materials akin to plant hormones, promoting plant growth and adapting to environmental conditions. |
|
Food Industry Importance |
L-glutamic acid, a non-essential amino acid, is naturally present in various foods either in free form or bound with proteins. It is extracted from sources like wheat gluten, soybean meal, and casein, or produced through microbial fermentation. In the food industry, it serves as a flavor-enhancing additive, commonly known as monosodium glutamate (MSG), added to foods such as soups, meats, seasonings, snacks, and sauces for taste enhancement. |
|
Role as Precursor |
L-glutamic acid acts as a precursor for the synthesis of proline, an essential amino acid crucial for collagen structure. |
|
Metabolism in Living Organisms |
Being an amino acid, L-glutamic acid can be easily metabolized by living organisms in soil and plants. |
|
pH-sensitive Properties |
Glutamic acid exhibits distinctive pH-sensitive properties, existing in different forms such as zwitterions, glutamate anions, and double-negative anions depending on the pH of the environment. |
|
General Description |
L-Glutamic acid (alpha) is a key excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, playing a crucial role in neuronal signaling, synaptic plasticity, and memory consolidation. It serves as a precursor for the synthesis of various bioactive compounds, including glutamate receptor antagonists and agonists, which are explored for treating neurological disorders such as persistent pain, Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and ischaemia. Its derivatives, including conformationally restricted analogues like 4-amino-4-carboxyproline and phosphinic analogues, are studied for their receptor specificity and therapeutic potential. Additionally, L-glutamic acid is utilized as a chiral template in stereocontrolled polymer synthesis, contributing to the development of crystalline polyamides. Its structural versatility enables applications in medicinal chemistry, neuroprotection, and the synthesis of bioactive molecules targeting glutamate receptors. |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H12N2O2/c6-4(3-8)1-2-5(7)9/h4,8H,1-3,6H2,(H2,7,9)
Surfactins are natural biosurfactants wi...
Stereoselective inhibition of the nuclea...
Main observation and conclusion: We desc...
Caged compounds are molecules that relea...
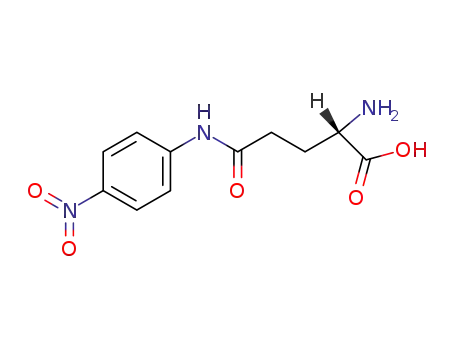
L-glutamic acid 5-(4-nitroanilide)

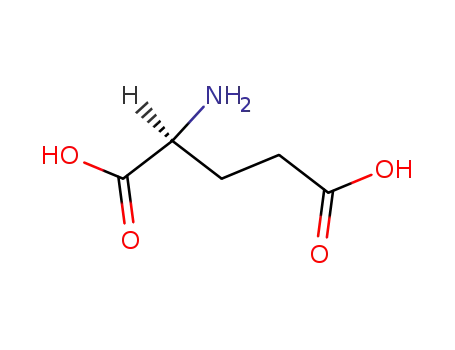
L-glutamic acid
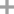
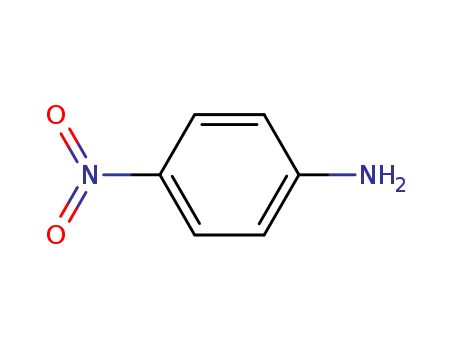
4-nitro-aniline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
marine bivalve lysozyme; MOPS buffer; Tapes japonica;
at 37 ℃;
pH=7.0;
Enzyme kinetics;
|
|
|
With
recombinant Pseudomonas nitroreducens IFO12694 γ-glutamyltranspeptidase;
at 30 ℃;
for 0.0333333h;
pH=10.5;
aq. buffer;
Enzymatic reaction;
|
|
|
With
C-terminal hexahistidine-tagged Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2 γ-glutamyl transpeptidase;
at 52 ℃;
pH=8;
Kinetics;
aq. Tris-HCl buffer;
Enzymatic reaction;
|
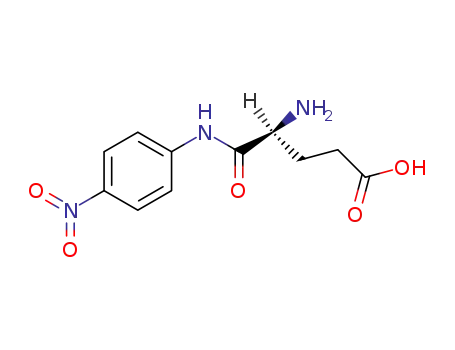
α-glutamyl p-nitroanilide


L-glutamic acid


4-nitro-aniline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
soybean cotyledon N-terminal acidic amino acid-specific aminopeptidase;
at 37 ℃;
pH=7.2;
aq. HEPES buffer;
Enzymatic reaction;
|
|
|
With
zinc(II) chloride;
at 37 ℃;
Reagent/catalyst;
Kinetics;
Tris-HCl buffer;
|
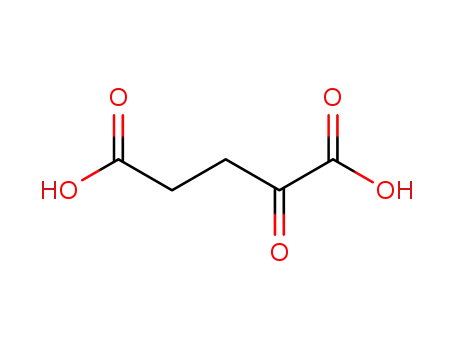
α-ketoglutaric acid
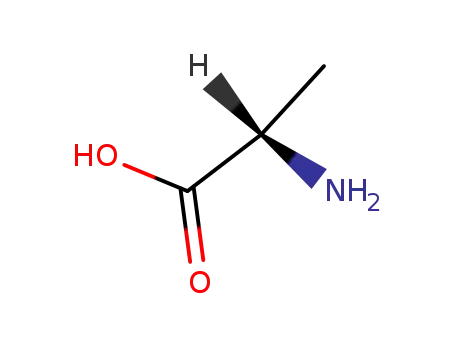
L-alanin
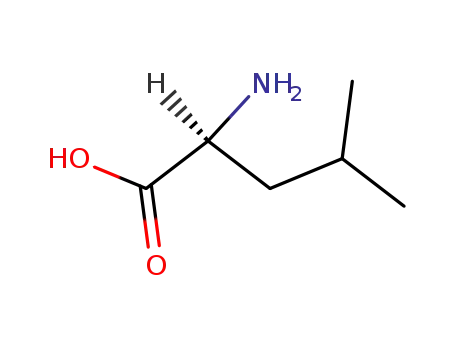
L-leucine
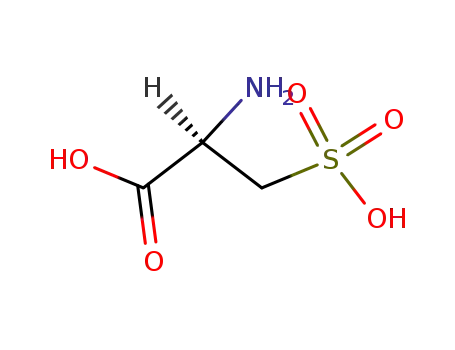
L-Cysteic acid
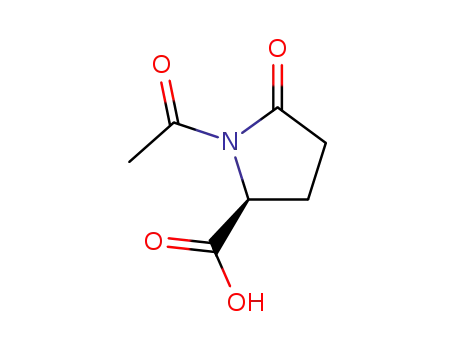
(S)-1-acetyl-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
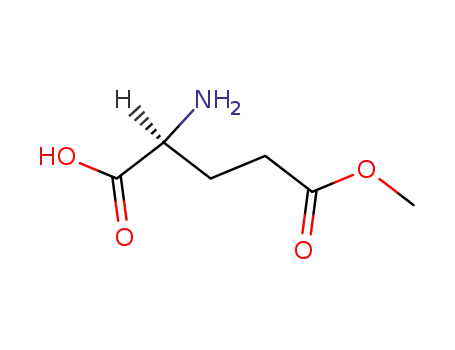
L-glutamic acid 5-methyl ester
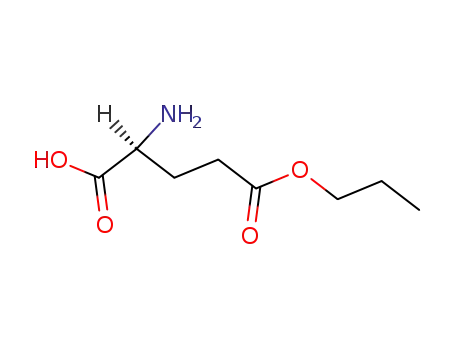
L-glutamic acid-5-propyl ester
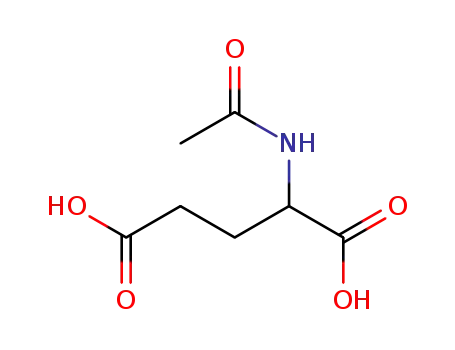
Acetyl-D,L-glutaminsaeure