Your Location:Home > Products > API > N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine
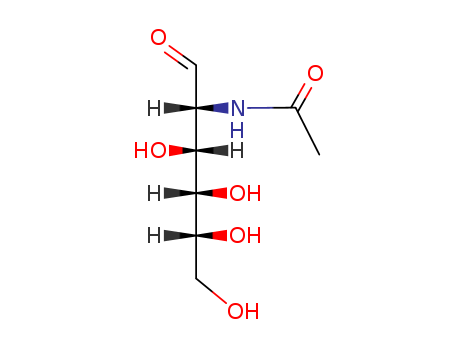


CasNo: 7512-17-6
MF: C8H15NO6
Appearance: white crystalline powder
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) oligomer may have the ability to initiate factors for canine polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) in vivo. It possesses wound healing and chemotactic activity. GlcNAc and its derivatives are usually employed in preparing dietary supplements and also used in therapeutic development. |
|
Sources |
N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) is derived from chitin, the most abundant nitrogen-containing biopolymer on Earth. Chitin can be found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans and insects, as well as in fungal cell walls.[1] |
|
Chemical Composition and Structure |
GlcNAc is a deacetylated derivative of glucosamine and is a major structural component of cell walls in bacteria and the extracellular matrix in animal cells. Its chemical structure consists of a glucose molecule with an N-acetyl group attached to the amine group.[2] |
|
Production Methods |
Microbial fermentation, particularly using engineered strains of Corynebacterium glutamicum, has emerged as a promising method for GlcNAc production.[3] |
|
General Description |
N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (GlcNAc) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose, where the hydroxyl group at the C-2 position is replaced by an acetamido group. It serves as a key precursor in the synthesis of biologically important molecules such as N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) and lipo-chitooligosaccharides like Myc-IV, which play roles in glycoconjugate function and symbiotic plant-fungal interactions, respectively. Additionally, GlcNAc derivatives have demonstrated neuroprotective effects, mitigating apoptosis in PC12 cells under stress conditions, highlighting their potential therapeutic applications in ischemic stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: The pyranose form of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. |
InChI:InChI=1/C8H15NO6/c1-4(12)9-5(2-10)7(14)8(15)6(13)3-11/h2,5-8,11,13-15H,3H2,1H3,(H,9,12)
Eleven glycosyl coumarylthiazole derivat...
Abstract: A new series of glycosyl benzo...
Several glycoconjugates of the diterpeno...
Bioproduction of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine ...
![3-O-{α-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-2-(acetamido)-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranosyl}echinocystic acid 28-O-{β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→3)-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→2)-[2-O-cinnamoyl-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→4)]-6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl} ester](/upload/2025/8/d57a68cb-87aa-4ed1-93ce-3d96b9424f7b.png)
3-O-{α-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-2-(acetamido)-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranosyl}echinocystic acid 28-O-{β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→3)-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→2)-[2-O-cinnamoyl-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→4)]-6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl} ester

D-xylose
D-apiose

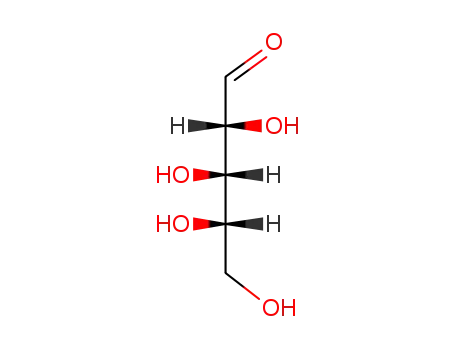
L-arabinose

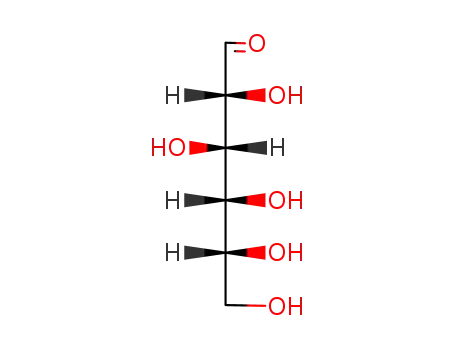
D-glucose

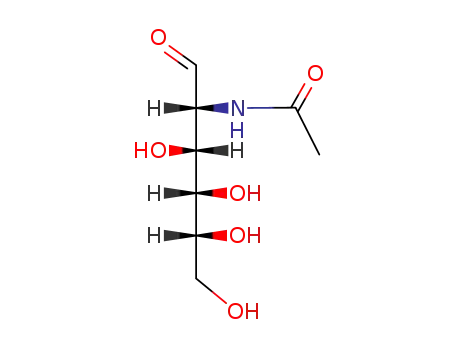
2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose

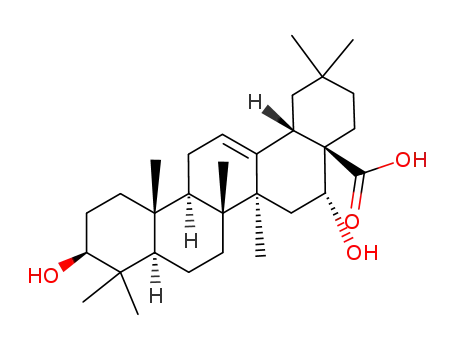
echinocystic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; water;
at 85 ℃;
for 2h;
|
![3-O-{α-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-2-(acetamido)-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranosyl}echinocystic acid 28-O-(β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→3)-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→2)-{2-O-[(6S,2E)-2,6-dimethyl-6-hydroxy-2,7-octadienoyl]-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→4)}-6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl) ester](/upload/2025/8/77c86503-a470-4930-bb10-e315eb54f4ca.png)
3-O-{α-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-2-(acetamido)-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranosyl}echinocystic acid 28-O-(β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→3)-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→2)-{2-O-[(6S,2E)-2,6-dimethyl-6-hydroxy-2,7-octadienoyl]-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→4)}-6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl) ester


D-xylose


D-apiose


L-arabinose


D-glucose


2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose


echinocystic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; water;
at 85 ℃;
for 2h;
|
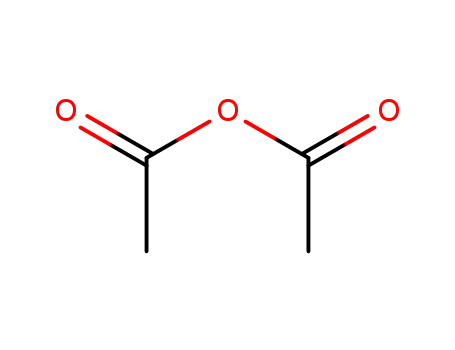
acetic anhydride
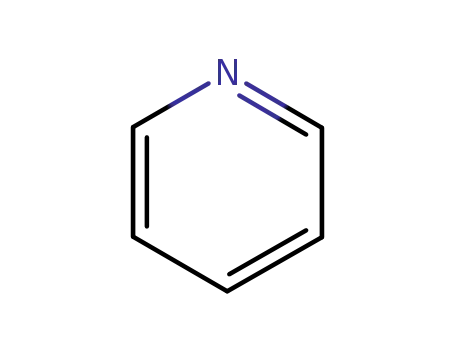
pyridine
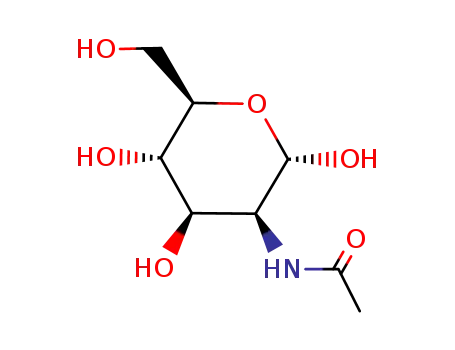
N-acetyl-D-mannosamine
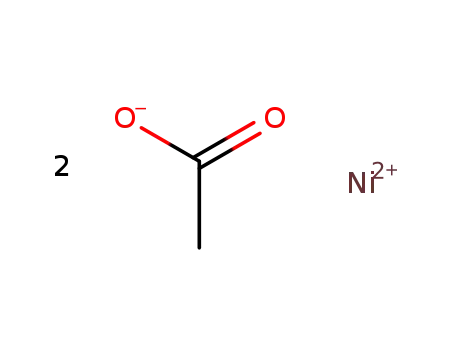
nickel diacetate
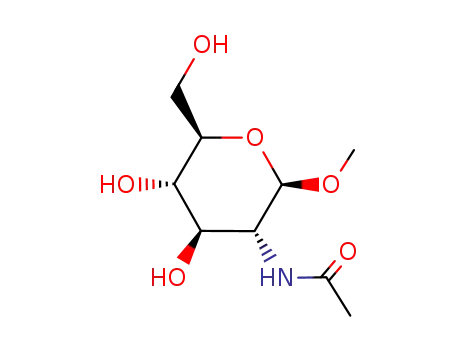
methyl N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide
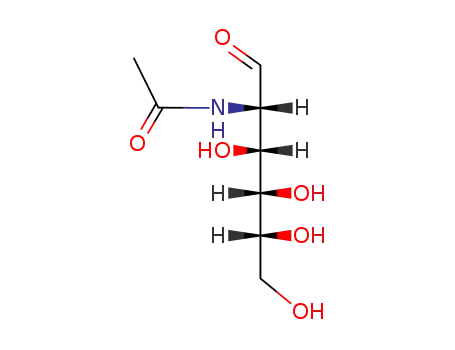
N-acetyl-D-mannosamine
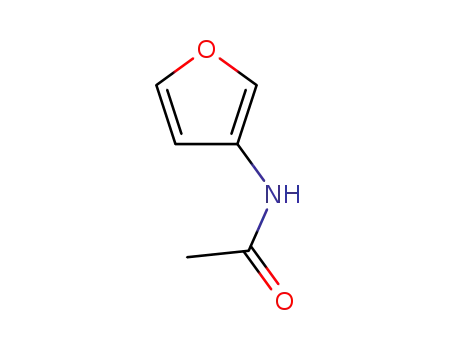
N-(furan-3-yl)acetamide
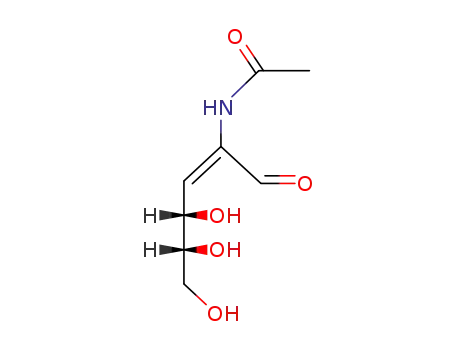
2-acetylamino-D-erythro-2,3-dideoxy-hex-2c-enose